What is plant-based diet?
A plate full of leafy greens like cabbage, kale, broccoli, and lettuce was what I pictured when I first heard of plant-based diets. It did not occur to me that it included other foods from plants until I thought deeper about it. Plant-based diet is simply foods gotten from plants, like grains, cereals, legumes, tubers, vegetables, and fruits. It does not necessarily mean being vegetarian or vegan. It means a larger part of a person’s diet, especially protein, is from plant source.
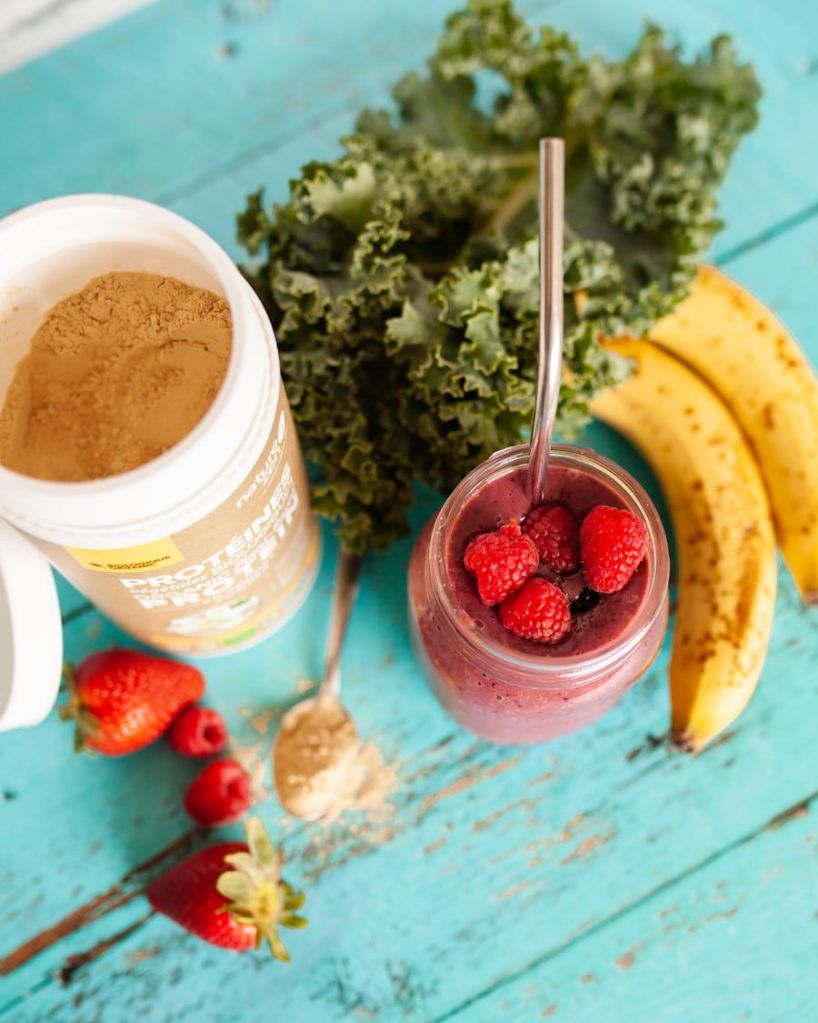

People are becoming more conscious of how what they eat affect their health. When traced back, it was discovered that our fore fathers who were very healthy and strong fed on mostly on plant-based diets. Today, many health problems have been linked to poor diet and consumption of too much of animal protein like meat, especially red meat. Plant-based diet is becoming more popular in the food industry as for many reasons.
Some of these reasons include:
- Environmental benefits: Livestock production generates greenhouse gas emissions (methane and nitrous oxide) and leaves carbon footprints, which contributes to climate change. Because of this, plant-based diets has been opted for since it is more sustainable and its production does not emit greenhouse gases.
- Animal rights: Another reason plant based diet has become a trend is the concern about animal cruelty. In some countries where animal rights is taken seriously, plant-based eating is becoming very popular. Telling Nigerians that they should stop or reduce consumption of animal protein because of animal rights will simply not work, you will probably get laughs or multiple ancestral stares. This is because animal rights is not considered important in the country. The best way to get Nigerians to have more consideration for protein from plant source over animal protein is to do it from a stand point of health benefits and economic benefit.
- Health Benefits: A balanced plant-based diet can help reduce the risk of heart-diseases, type 2 diabetes, skin problems, and helps with weight management. Also, plant-based diet has been shown to lower symptoms of depression and improve mood.
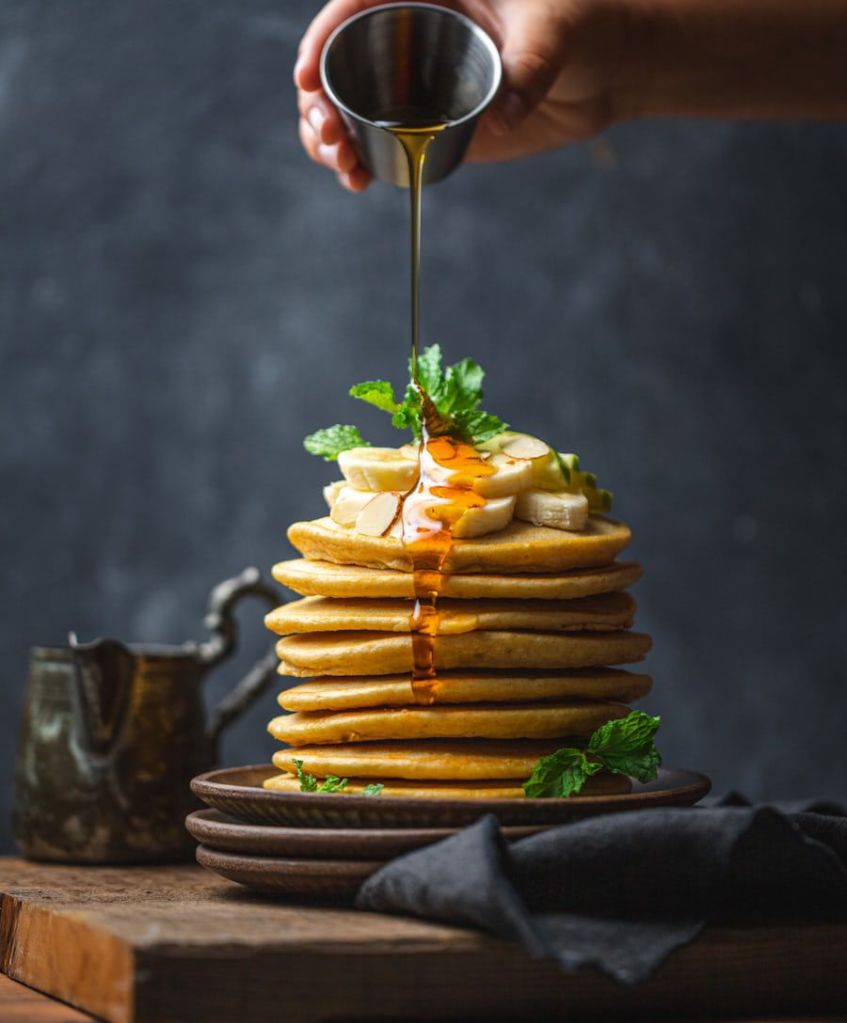

It is interesting to know that the Nigerian diet largely consists of food sourced from plants, like rice, beans, yam, millet, sorghum, peanuts, cashew nuts, potatoes, and vegetables. In Nigeria, the percentage of animal-based diet consumption is lower than plant-based diet consumption. Although, while most of the Nigerian diet is plant based, there is much reliance on animal protein as a source of protein. When an average Nigerian thinks protein, what comes to mind is one of these: egg, fish, meat or chicken.
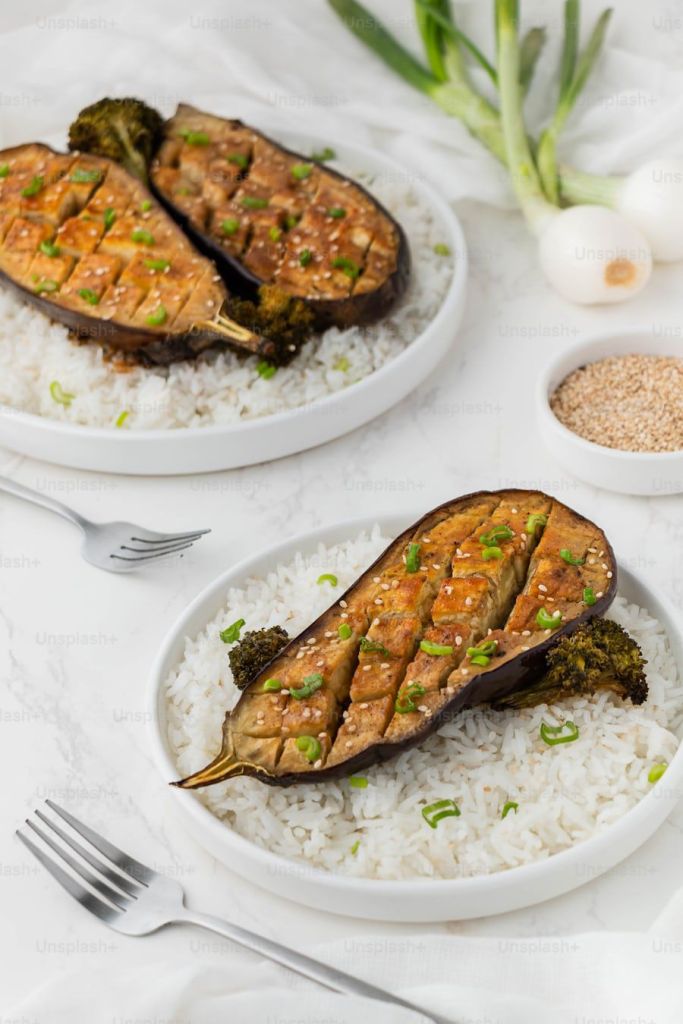

Animal protein cannot be totally eradicated from the Nigerian diet. I mean what is Owanbe (party) without surplus meat? What is Amala and ewedu without ogufe (goat meat)? It is a culture!
Meat serves as an encouragement to eat a meal across the states in Nigeria. Persuading Nigerians to embrace plant-based eating, especially eating more of plant protein than animal protein will take some effort. There are various factors that play a key role in influencing Nigerians to embrace plant-based eating, they include:
- Family background- Everyone ate what they were fed growing up and food habits were developed overtime. Family orientation in terms of feeding habits determines a person’s feeding habit and pattern. Most Nigerians grew up eating meals like rice and beef/fish stew, Eba/fufu/Amala and soup with beef/fish, yam and egg, bread and egg, akara and pap with milk, beans and garri/pap/ bread, suya and so on. While most of these meals are plant based, it is usually accompanied with one or more animal protein. So, to an average Nigerian, a meal might be incomplete or less satisfying without animal protein.
- Social Status- Eating without meat or any animal protein is considered a sign of poverty. Wealthy people consume more animal protein than the poor. It is more of a status thing than a health thing. You will hear some people say something like, “how can I eat food without meat?” “How can I eat only one meat? It is too small for me, I have moved pass that level.” Because of this, plant-based options might seem less desireable. Mindset about animal protein is mostly linked to status and that has to change for plant protein to be embraced. Cultural snd social acceptance of plant-based eating should be promoted.
- Education- Not many people aware of what they consume and how it affects them. Today, both the young and elderly are more health conscious and they want to know how to be healthier. More education about plant-based diet can enlighten Nigerians about its importance and how it benefits them. Educational institutions can incorporate plant-based nutrition into the curricula to educate younger/future generation on the benefits of healthy eating. Social media campaigns encouraging Nigerians to eat more of fruits, vegetables and plant protein will go a long way to help them embrace eating plant-based diet.
- Food Supply- Due to the high rise of food insecurity in the nation, people might give more priority to food that is accessible over adopting a specific diet like plant-based eating. Policies that support the increased availability and accessibility of plant-based foods should be implemented.
- Income- In an average Nigerian family, most meals are taken with animal protein. Due to the economic hardship in the country many people cannot afford to eat meat, fish and eggs because animal protein is expensive. Many families have had to adjust by reducing animal protein consumption because of the high cost and low income. Still, many of the plant-based foods like rice, yam, and beans are still not affordable to many Nigerians, especially the low-income earners. Affordable prices of plant-based protein can help low-income earners embrace plant-based eating.
- Government Policies- The government has an important role to play in the diet of its people. If the government prioritizes animal agriculture over plant-based farming, it will pose a challenge to the adoption of plant-based eating in Nigeria.They can create policies that encourage production of plant-based foods and ensure they are affordable in a way that benefits both farmers and consumers. Some suggestions are:
1. Provision of subsidies to farmers in order to make plan-based products more affordable.
2. Prioritization of plant-based meal options in public institutions like schools and hospitals.
3. Update national dietary guidelines to favor consumption of more plant-based products.
YES! Nigerians can embrace plant-based eating if these factors are carefully considered. Still, it will take some intentionality on the part of Nigerians to fully embrace plant-based eating.

Leave a comment