
You are what you eat.
The majority of the world’s population consumes a surprisingly low amount of plant-based foods. The convenience of chemically processed foods, with their long shelf life and ease of consumption, has led many down a path of unhealthy eating. However, this trend comes with a price: the toxins and preservatives in these foods can have devastating effects on human health, ultimately shortening our lifespan.
In this article, we’ll explore the numerous health benefits of adopting a plant-based diet and examine whether making the switch is truly worth it.
What is a Plant-Based Diet?
A plant-based diet is a dietary pattern that focuses on consuming high amounts of fiber-rich plant foods and low amounts of animal products. This diet encompasses a wide range of eating habits, including vegan and vegetarian options.
Key Components of Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets emphasize whole, minimally processed foods from plants, including:
1. Vegetables
2. Fruits
3. Whole grains
4. Legumes (beans and pulses)
5. Nuts and seeds
6. Herbs and spices
Flexibility of Plant-Based Diets
While plant-based diets may be vegan or vegetarian, they don’t have to be. These diets are defined by a high frequency of plant food consumption and a low frequency of animal food consumption, allowing for flexibility and personalization.
Here Are 10 Benefits of Eating Plant-Based Foods.
1. Boost the Immune System: It supports your immune system. Plants have essential nutrients that you cannot get from other foods. The vitamins and minerals, phytochemicals and antioxidants in plants help keep your cells healthy and your body in balance so that your immune system can function at its best.
“Plants give your body what it needs to help fight off infection,” says Andrea Murray, MD Anderson health education specialist. “A plant-based diet strengthens your immune system to protect you against germs and microorganisms.”
2. Increase Fiber: Plants are high in fiber. Fiber is present in all unprocessed plant foods. It is what makes up the structure of the plant, and if you eat more of it you access a whole host of benefits.
Eating a plant-based diet improves the health of your gut so you are better able to absorb the nutrients from food that support your immune system and reduce inflammation. Fiber can lower cholesterol and stabilize blood sugar and it’s great for good bowel management.
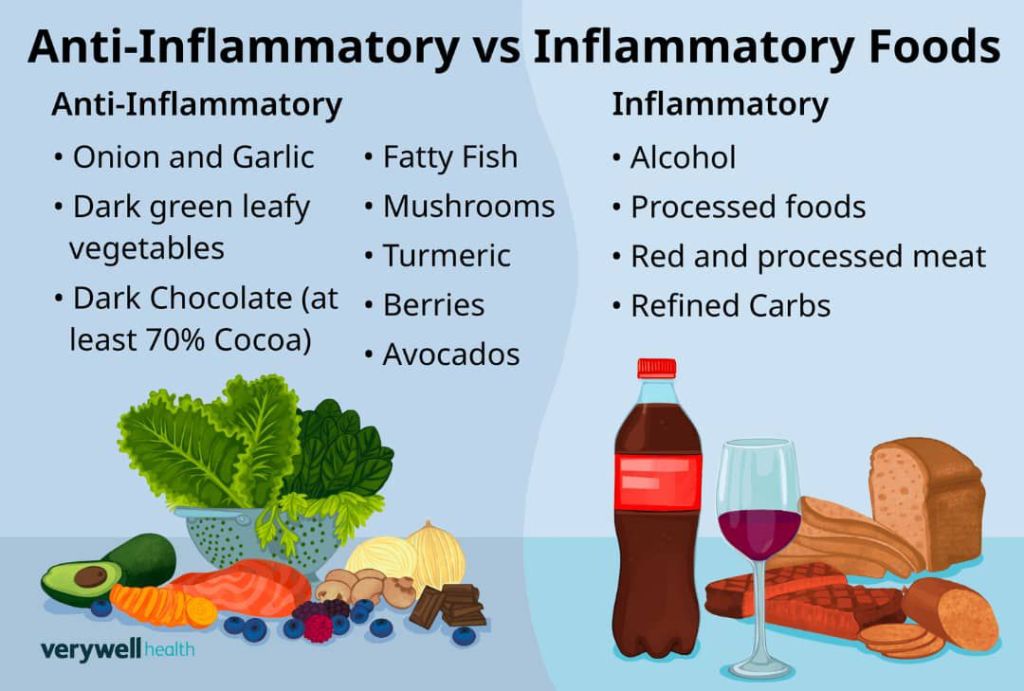
3. Reduced Inflammation: Plant foods reduce inflammation. Plants’ essential nutrients work to resolve inflammation in your body. The same tiny phytochemicals and antioxidants that boost your immune system also go around your body neutralizing toxins from pollution, processed food, bacteria, viruses and more.
“Antioxidants in plants grab all these so-called free radicals that can throw your body off balance” . “To reduce inflammation, it’s important to eat plant-based and to listen to your body’s signals for how foods work for you.”
Prolonged inflammation can damage your body’s cells and tissue and has been linked to cancer and other inflammatory diseases like arthritis. A plant-based diet may protect you because it removes some of the triggers to these diseases.
4. Weight Management: Your risk of obesity decreases when you swap a meat-heavy diet for a plant-based one. In short: Plant eaters tend to weigh less, even if that’s not always the No. 1 goal. “The idea is to nourish the body and cells to improve health outcomes, but weight loss may be a by-product of replacing and reducing certain foods”. The aforementioned Diabetes Care study found substantial body mass index (BMI) differences between non-meat eaters and meat eaters. The mean BMI for vegans was 23.6, while for ‘non vegetarians’ it was 28.8, which qualifies as overweight, according to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Eating more plants can help you drop pounds, too. A small study found that 65 overweight adults who followed a whole-food, plant-based diet for one year lost 9.25 pounds on average. Plus, this diet was not calorie-restricted; the participants were allowed to eat what they wanted and still lost weight.
One reason for the weight loss is that whole grains and vegetables are relatively low on the glycemic index — which means they’re digested more slowly — and fruit contains antioxidants and fiber, which helps prolong fullness, according to research. It’s incredibly important to prioritize healthy, quality plant-based foods if weight loss is your goal. “Someone can eat a very healthy plant-based diet, but they can also eat a very unhealthy plant-based diet.”
5. Balance Cholesterol Intake: High cholesterol can lead to fatty deposits in the blood, which can restrict blood flow and potentially lead to heart attack, stroke, or heart disease. But a healthy diet can help keep cholesterol levels in check. Specifically, moving away from a diet filled with animal products toward one that’s primarily plant based can lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol by between 10 and 15 percent, while those following a strict vegan diet can lower their LDL cholesterol by as much as 25 percent.
6. Improved Heart Health: Heart disease is one of the leading cause of death in the world today, with one person dying every 33 seconds. High cholesterol and high blood pressure are the biggest risk factors for heart disease, along with diabetes, obesity, physical inactivity, smoking, and excess alcohol use.
Saturated fats are highest in red meat, cheese, whole milk, butter, ice cream, lard, fried foods, and baked goods. Diets high in these fats are pro-inflammatory and can lead to elevated LDL cholesterol levels (aka “bad” cholesterol). These sources are naturally reduced and replaced with healthier fat sources when following a whole food plant-based diet.
Some of the best plant-based fat sources for heart health are:
Avocados, walnuts, flax seeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, olive oil.
A diet low in saturated and trans fats is associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and certain types of cancers. Replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats (particularly omega-3s) and high-quality carbohydrates reduces the risk of heart disease. Additionally, soluble fiber, which can only be found in plant-based foods, can help lower LDL-cholesterol.
While there has been some recent controversy on whether or not saturated fats are as bad as we’ve thought, the majority of research still backs the harmful effects of diets high in saturated fat.
7. Environmental Sustainability: The majority of meat and dairy produced today, come from factory farms. Animal agriculture contributes greatly to the use of natural resources, CO2 emissions, and antibiotic resistance.
Going fully plant-based may not be an option for you at this time depending on your current situation. However, adding more plant foods to your diet and decreasing your overall meat consumption even slightly can benefit your health and the environment.
A 2018 study found that a vegan diet had the lowest environmental impact, followed by vegetarian diets, and then diets that included varying amounts of meat.
Another study published in 2018 found that shifting to a plant-based diet could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and land use requirements for food production, and could help to mitigate climate change.
Plant-based diets can also have benefits for water conservation, biodiversity, and other aspects of environmental sustainability. The reduction in environmental footprint was proportional to the degree of animal product avoidance.
8. Enhance Blood Sugar: Plant-based diets can play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Research indicates that plant-based diets can improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body use glucose more effectively.
Many plant-based foods have a low glycemic index, meaning they cause a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. This can help prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar. Since plant-based diets promote weight loss and maintenance, they can be particularly beneficial for individuals with or at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.

9. Improve Athletic Performance: Athletes are increasingly turning to plant-based diets to enhance their performance and recovery. Plant-based diets are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, which can help reduce muscle soreness and speed up recovery after workouts.
A diet rich in whole foods provides the necessary carbohydrates and nutrients to fuel athletic performance.
Many professional athletes, attribute their success to plant-based diets, showcasing the potential benefits for physical performance.
10. Longevity: Adopting a plant-based diet may contribute to a longer, healthier life. By lowering the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers, a plant-based diet can enhance overall. A diet rich in nutrients can help support healthy aging, maintaining cognitive function and physical health as you age. Research has shown that populations with plant-based diets, such as those in the Mediterranean region, tend to have lower mortality rates and longer life expectancies
Is Eating Plants The Way Out?

Eating plant-based does not mean you can’t eat meat. It means your meals are mostly plants: vegetables, whole grains and fruits. Beans, seeds and nuts are also included.
Even a plant-based meal relies on you to avoid the major diet pitfalls, like sugar and fat.
The Sustainable Way Out.
Using healthy cooking methods and knowing how to make the most of your vegetables can help you get all the benefits a plant-based diet offers.
Fill two-thirds of your plate with these plant-based foods.
The remaining one-third should be a lean protein like chicken or fish, or a plant protein beans.
This means deep-fried vegetables are out. So are highly processed foods like crackers and cookies.
Limit sugary desserts as well and make sure you are picking whole grains. Regular pasta, white bread and white rice may be plant products, but they are not made from whole grains. Choose 100% whole wheat pasta and bread, and eat brown rice.
Conclusion.
As you can see, the benefits of a plant-based diet involve several systems of the body, including improvements in cholesterol, blood pressure, diabetes, inflammation, kidney health, gut health, and cancer risk.
Does this mean everyone who eats meat will get a chronic illness? Of course not.
I wholeheartedly believe in intuitive eating, which involves eating what is right for you. However, the science behind the benefits of a plant-based diet can be used as gentle nutrition guidance for you on your intuitive eating journey.
Choosing plants will help all your body’s systems work the best they can.

Leave a comment